Disclaimer: We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. For more information, visit our Disclaimer Page.
Design Thinking is a strategy to create breakthrough ideas. It’s been adopted by many major brands like Apple, Google, Samsung, and GE to stay relevant in their product line-ups.
One of the most significant benefits of design thinking is that it helps leaders envision how they want their company to be in the future without being constrained by current realities or past successes. This innovative perspective allows for new possibilities and leads to more quantifiable results and better customer satisfaction and engagement because these insights are often based on actual needs.
Nowadays, it isn’t uncommon to find design thinking taught at well-known universities such as Stanford University or Harvard Business School; but what exactly does design thinking entail?
In this blog post, we will explore what design thinking is, how you can use it to drive success for your company, and some of its benefits.
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a structured problem-solving approach focusing on the user’s needs. It’s a way of thinking that allows you to come up with innovative solutions to problems by breaking traditional thinking patterns and looking at things from different angles.
It can be used in all sorts of different circumstances, from designing a new product or service, redesigning an existing one, coming up with innovative ideas for marketing campaigns, and much more.
The basics of design thinking are pretty simple: you start by understanding the user’s needs, define the problem you’re trying to solve, generate ideas to solve that problem, prototype your solution, and then test it with real users. The process is iterative, so you keep repeating these steps until you arrive at a final solution that works well for your users.
This approach is different from the traditional scientific method, which starts with a hypothesis and tests it to see if it’s correct. Instead, design thinking is more flexible and allows for more creativity because it doesn’t require you to have all the answers upfront.
Design thinking has its roots in design, but it can be used in any field, whether designing a new product or service, developing a marketing campaign, or even solving personal problems.
Related: Experimentation
Benefits of Design Thinking
Design thinking has many benefits, both for individuals and organizations. Some of the benefits of design thinking include:
- Helps you understand your users: This approach helps you deeply understand them and their needs because it allows you to design products, services, and experiences that meet their needs and want.
- Increases satisfaction for both users and businesses: Users are happy because they get products, services, and experiences that meet their needs. And companies are happy because they are providing value to their customers.
- Generates new ideas: This creative approach allows you to create new ideas and solutions that you may not have thought of before.
- Improves collaboration: Design thinking helps improve collaboration between team members and businesses and their customers.
- Speeds up the innovation process: By using design thinking, you can speed up the innovation process and bring new products and services to market faster.
- Makes you more user-centric: This approach helps you focus on the user, which makes you more user-centric in your thinking and actions.
- Helps you solve complex problems: Design thinking can help you tackle difficult problems by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable pieces.
Related: Examples of Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
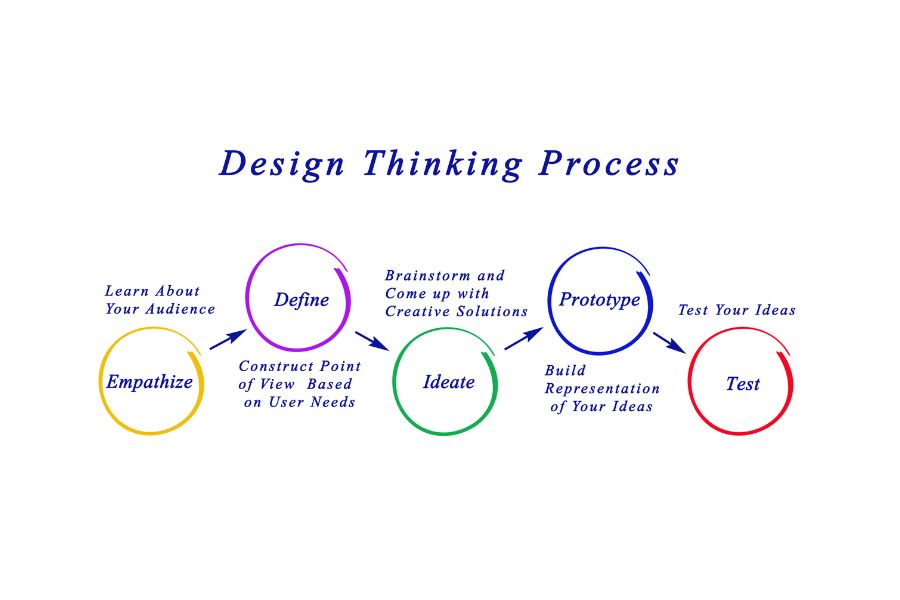
5 Stages of The Design Thinking Process
The Design Thinking process has many variants, some of which have 3-7 different stages. However, they all embody the same principles that Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon first described in The Sciences of the Artificial back in 1969.
The Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford, more commonly known as d.school, is the leading institute in applying and teaching design thinking to a wide range of industries based on their 5 phase model, which they described with these phases:
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
1. Empathize
The design thinking process begins by understanding the problem. This includes consulting with experts and immersing yourself in the physical environment to better understand the issue at hand. Without it, design thinking would not be as successful because it is the only way to set aside assumptions and gain insight into users and their needs.
This stage aims to gather as much information about the user and their needs. This includes creating surveys, talking with users in person or over a phone line, observing people using similar products, etc.
2. Define (the problem)
The define stage is the time to gather all your findings and observations from the empathizing process. Then, you’ll analyze what you’ve been able to find out so far, synthesizing it into a problem statement based in a human-centered manner.
In this stage, the designers will research and develop ideas for features that could solve user problems. One way they can do this is by asking questions like “What are some potential solutions?” or “Is there a better solution to our problem than what we have now?”.
3. Ideate
During the third stage of Design Thinking, designers are ready to generate ideas. You’ve grown to understand your users and their needs in the Empathise step; you’ve analyzed and synthesized your observations from the Define stage into a human-centered problem statement that reflects how people live day by day with those issues.
Brainstorming and Worst Possible Idea sessions are great tools for the beginning stages of problem-solving. They help with creativity, new ideas, and expanding our understanding of a difficult situation or task at hand. Getting as many ideas out there during these brainstorming sessions is essential because you never know what will work!
Ideation is an essential part of any creative process – from product development to art creation; it always starts somewhere, if not everything (even when discussing something like coming up with your next conversational topic). Brainstorms inspire us by throwing all sorts of crazy thoughts into the mix that might eventually lead us down some path towards whatever goal we have set ourselves to achieving course. Of course, the worst possible scenario can also be used as input.
It would be best if you got as many ideas or solutions to solve a problem in the Ideation phase and pick other techniques by the end to find out which one is best.
4. Prototype
After a product or specific feature is conceptualized, it may be necessary to design many scaled-down versions of the final production. These prototypes are then explored and tested for possible solutions with different components linked together.
Prototypes might be shared within the team and other departments outside that original department to identify which solution will work best. This phase can also include testing on small groups not involved during previous stages to get an unbiased opinion about what works best.
By the end of this stage, you’ll have a better idea if your product will work for customers and what needs to be changed.
5. Test
A critical component of the design process is to test different solutions and see which works best. Testing at this stage will often lead designers back into earlier stages to redefine problems or better understand users, needs, desires, feelings, etc.
The evaluators test the prototypes to see which is most effective, and then they proceed with total production if it has no flaws or constraints.
The five phases, stages, or modes are not always sequential. They can happen in parallel and have repeated iterations. Since the process is often iterative, you should consider it an overview of the various ways that innovation occurs rather than a step-by-step guide to how things go down when innovating for work.
Related: Benefits and Risks of Innovation
How to Use Design Thinking for Your Company’s Success
You can use design thinking to drive your company’s success in many ways. We’ve listed a few examples below:
- Improve creativity: Design thinking is a great way to tap into the creativity of your team members. By giving them the freedom to think outside the box, you’ll develop more innovative solutions to problems.
- Improve customer satisfaction: It helps you identify and solve your customers’ pain points. By understanding their needs and wants, you can create products, services, and experiences they’ll love.
- Increase employee satisfaction: By understanding their needs and wants, you can make changes that will improve their satisfaction and motivation.
- Increase sales: It can also be used to increase sales. Creating a better customer experience will make customers more likely to buy from you again.
- Improve efficiency: Design thinking can also help you streamline your processes and make them more efficient. By understanding your customer’s needs, you can eliminate steps that aren’t necessary and make it easier for them to get what they need.
- Reduce costs: By streamlining your processes and making them more efficient, you’ll be able to save money.
- Developing marketing campaigns: This is done by understanding people’s needs and wants and then generating ideas for how to reach those people with your marketing message.
The process is iterative, which means you keep repeating the steps until you arrive at a final solution that works well for your users.
Related: How do Companies Encourage Innovation
Examples of Design Thinking in Action
Design thinking has been used by some of the world’s most successful companies to create innovative products, services, and experiences. We’ve listed a few examples below:
Netflix

Netflix is an entertainment company that has been blazing its path for the last few decades. They are one of the most prominent players in this industry and have innovative design thinking to thank for their success.
Their business centers around personalized content delivery, which means they use a powerful recommendation engine to serve users with engaging media while staying focused on what makes them unique: customer satisfaction through personalization.
This dynamic approach shows how Netflix constantly improves upon their original idea by leveraging innovations and techniques over time; it’s something we can expect from them from now on as well!
Airbnb

The article “How Design Thinking Transformed Airbnb from a Failing Startup to a Billion Dollar Business,” published in First Round Review, outlines how the famed startup went from $200 profit per week to what it is today.
Airbnb was born out of necessity when Joe Gebbia and Brian Chesky struggled to pay rent in San Francisco. They saw an opportunity for a hospitality revolution once they put up their first iteration of the service but had one problem that needed solving: researching users’ travel preferences.
Young millennials are educated, financially stable, and want to stay in a comfortable environment; Airbnb found that appealing to these affluent customers with unique experiences instead of hotel guests on its site became more popular than ever before! Now you can rent a space from locals worldwide on this platform which has become a traveling agent!
IBM

IBM, one of the world’s largest corporations and global companies, has seen a 301% ROI by banking on design thinking. Designing for user experience is something that IBM takes seriously—they have their internal design team to ensure everything they do aligns with this philosophy.
To promote innovation outside of just production processes and product development cycles (aka “the way things are done around here), an open toolkit was created to give everyone opportunities for growth through creativity and new ideas–even if you’re not technically minded or from a technology background!
Uber

The UberEATS team has a design thinking mindset that allows them to offer food in cities worldwide. One of their top takeaways from this article is how there’s no “one size fits all” way for everyone. It takes empathy with your customer base to make any progress addition; the company is committed to understanding its products and the places where they are sold.
Bank of America
Bank of America has a history in design thinking, going back to its partnership with IDEO. They ultimately rolled out the Keep The Change program, which solved an issue that customers had been facing for years: rounding up on checks and not saving any money! This initiative came from research done by IDEO, where they found savers were intentionally doing this, but there was no way for them to easily keep track of it all or use those funds elsewhere- until now.
“Empathy is at the heart of design. Without the understanding of what others see, feel, and experience, design is a pointless task”.
TIM BROWN
Related: Benefits of Research and Development
Conclusion
Design thinking is a powerful innovation strategy that can be used to drive success for your company. By understanding the needs of your users and generating creative solutions to meet those needs, you can create products, services, and experiences that are both user-friendly and successful. Design thinking is a win-win for everyone involved.
Design thinking is a powerful innovation strategy, but it’s not the only one. What other innovation strategies do you know of? Share your thoughts in the comments below.





