Disclaimer: We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. For more information, visit our Disclaimer Page.
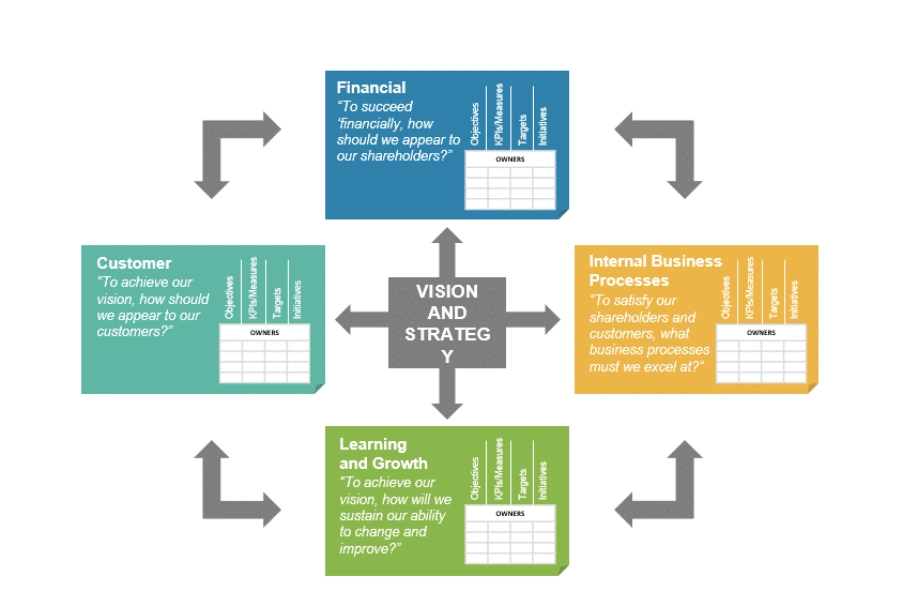
The Balanced Scorecard strategy is a powerful tool that can unlock success for businesses by enabling effective strategic planning and execution, leading to enhanced organizational performance. This approach provides a holistic view of an organization’s performance across four key areas: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
By implementing the Balanced Scorecard (BSC), organizations can define strategic objectives and align metrics with their goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to track progress in each perspective, such as revenue growth rate, customer satisfaction score, cycle time, and employee satisfaction score. This data-driven approach helps organizations make informed decisions and drive growth.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard improves strategic communication, aligns the workforce, and prioritizes projects. It also enhances organizational alignment, drives accountability, and shows employees how they contribute to the organization’s success. With the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can make better decisions, improve underperforming areas, and adapt to changes in the market.
Key Takeaways:
- The Balanced Scorecard strategy enables effective strategic planning and execution.
- It provides a holistic view of organizational performance across four key areas.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to track progress and make data-driven decisions.
- Implementing the Balanced Scorecard improves strategic communication and aligns the workforce.
- Balanced scorecard software, like Spider Impact, enhances the benefits of implementing the BSC.
Understanding the Balanced Scorecard Approach
The Balanced Scorecard approach is a comprehensive framework that allows businesses to measure and improve performance, aligning their business processes with strategic objectives to create a robust management system.
By adopting this approach, organizations can gain a holistic view of their performance, evaluating it from four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. This balanced approach enables businesses to assess various aspects of their operations and make data-driven decisions to drive growth.
Measurement is a critical component of the Balanced Scorecard approach. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to track progress in each perspective. For example, businesses can track metrics such as revenue growth rate, customer satisfaction score, cycle time, and employee satisfaction score to gauge their performance across different areas of their operations.
| Perspective | Key Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue growth rate, Return on investment (ROI) |
| Customer | Customer satisfaction score, Net Promoter Score (NPS) |
| Internal Processes | Cycle time, Quality defect rate |
| Learning and Growth | Employee satisfaction score, Training hours per employee |
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard approach offers several benefits. It improves strategic communication by providing a common language and framework for discussions. It aligns the workforce by clearly defining strategic objectives and the metrics used to measure progress. It also helps prioritize projects and initiatives based on their alignment with strategic goals.
Enhancing the Benefits with Balanced Scorecard Software
Using a comprehensive software solution, such as Spider Impact, enhances the benefits of implementing the Balanced Scorecard approach. It simplifies the process of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing performance data, making it easier for organizations to track progress and make informed decisions. With features like interactive dashboards, data integration, and automated reporting, businesses can gain real-time insights and drive performance improvement more effectively.
The Balanced Scorecard approach provides businesses with a strategic framework for measuring and improving performance. By aligning business processes with strategic objectives, organizations can create a robust management system that facilitates data-driven decision-making and supports growth. Implementing balanced scorecard software further enhances the benefits, enabling businesses to streamline performance measurement and gain actionable insights for continuous improvement.
Related: David Norton
Key Elements of the Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard incorporates key elements such as strategic goals, performance objectives, and the use of key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and drive performance improvement, ultimately fostering a culture of total quality management.
Strategic goals are the overarching objectives that organizations aim to achieve. They provide a clear direction for the entire workforce and help align efforts across different departments and functions. By defining strategic goals, organizations can focus their resources and efforts on what truly matters and drive progress toward their desired outcomes.
| Strategic Goals | Performance Objectives | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | Increase sales by X% | Revenue growth rate |
| Customer Satisfaction | Improve customer satisfaction score from X to Y | Customer satisfaction score |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduce cycle time by X% | Cycle time |
| Employee Engagement | Increase employee satisfaction score from X to Y | Employee satisfaction score |
Performance objectives are specific targets that organizations set to measure progress toward their strategic goals. These objectives provide clarity and focus on what needs to be accomplished and help prioritize efforts and allocate resources effectively. Each strategic goal may have multiple performance objectives based on the different aspects and dimensions of the goal.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the metrics used to measure performance and track progress towards achieving performance objectives. KPIs provide tangible and measurable data that organizations can use to assess their performance and make informed decisions. Examples of KPIs include revenue growth rate, customer satisfaction score, cycle time, and employee satisfaction score. By monitoring these KPIs, organizations can identify areas of improvement and take corrective actions to drive performance improvement.
Driving Performance with Total Quality Management
The use of the Balanced Scorecard as a strategic management tool fosters a culture of total quality management (TQM). TQM is an approach that emphasizes continuous improvement, customer focus, and employee engagement. By incorporating TQM principles, organizations can enhance their performance in all perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard and drive overall organizational success.
TQM encourages organizations to focus on delivering high-quality products and services, meeting customer expectations, and continuously improving processes and operations. It promotes a proactive approach to problem-solving and encourages employees to take ownership of their work and contribute to the organization’s success. TQM also fosters a culture of collaboration and teamwork, where employees from different functions and levels work together towards shared goals.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard with a focus on TQM allows organizations to align strategic goals, performance objectives, and KPIs with the principles of quality management. It provides a framework for organizations to measure their performance holistically, identify areas for improvement, and drive performance enhancement across all aspects of the business.
The Four Perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard framework consists of four crucial perspectives – financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth – allowing organizations to gain a comprehensive and balanced view of their performance and make informed strategic decisions.
Financial Control: This perspective focuses on measuring and monitoring financial performance indicators that directly contribute to organizational success. Key metrics may include revenue growth rate, return on investment (ROI), cost management, and profitability. By analyzing financial data, organizations can assess their financial stability, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to achieve their financial objectives.
Customer Perspectives: The customer perspective emphasizes measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty to understand how an organization is meeting customer needs and expectations. Metrics in this perspective may include customer satisfaction scores, customer retention rates, and market share. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, organizations can enhance their competitiveness, build strong customer relationships, and drive business growth.
Internal Operations: The internal processes perspective focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s internal operations. It involves measuring key performance indicators related to process quality, cycle time, cost management, and productivity. By examining internal processes, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and optimize performance to deliver high-quality products or services.
Learning and Growth: The learning and growth perspective emphasizes the development of employees and the organization’s ability to adapt and innovate. Key metrics may include employee satisfaction scores, training and development initiatives, and the organization’s capacity for innovation. By investing in employee growth and fostering a culture of continuous learning, organizations can create a skilled and motivated workforce, drive innovation, and stay ahead in a rapidly changing business environment.
Overall, the Balanced Scorecard framework enables organizations to assess their performance holistically and align their metrics with strategic objectives. By considering the financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, organizations can drive growth, improve efficiency, and achieve long-term success.
| Perspective | Main Focus | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Control | Measure financial performance | Revenue growth rate, ROI, cost management, profitability |
| Customer Perspectives | Assess customer satisfaction and loyalty | Customer satisfaction scores, customer retention rates, market share |
| Internal Operations | Evaluate internal process efficiency | Process quality, cycle time, cost management, productivity |
| Learning and Growth | Develop employees and foster innovation | Employee satisfaction scores, training initiatives, capacity for innovation |
Benefits of Implementing the Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard strategy brings numerous benefits to organizations, including enhanced organizational alignment, increased accountability, and better-informed decision-making, ultimately strengthening the implementation of strategic initiatives. The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) approach provides a holistic view of an organization’s performance across four key areas: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. By measuring performance in a balanced way, organizations can gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and success.
One of the key advantages of the BSC is its ability to improve organizational alignment. With clear strategic objectives and aligned metrics, employees at all levels are empowered to understand their roles and how they contribute to the organization’s overall goals. This alignment fosters a sense of unity and shared purpose, enhancing collaboration and driving performance across departments and functions.
Furthermore, the implementation of the BSC promotes increased accountability within the organization. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the four perspectives, such as revenue growth rate, customer satisfaction score, cycle time, and employee satisfaction score, organizations can hold individuals and teams accountable for their performance. This accountability creates a culture of ownership and responsibility, where employees are motivated to deliver results and contribute to the organization’s success.
In addition to alignment and accountability, the BSC enables better-informed decision-making. By providing a comprehensive view of organizational performance, with metrics and data from different perspectives, leaders can make strategic decisions based on accurate and relevant information. This data-driven approach minimizes guesswork and reduces the risk of making decisions based on incomplete or biased information, leading to more effective execution of strategic initiatives.
| Benefits of Implementing the Balanced Scorecard |
|---|
| Enhanced Organizational Alignment |
| Increased Accountability |
| Better-Informed Decision-Making |
Continuous improvement is a fundamental concept in the Balanced Scorecard approach. Here’s why it matters:
- Adaptation to Changing Market Conditions: Markets are dynamic, and businesses need to stay agile. Regular performance assessments allow organizations to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
- Efficiency Optimization: The internal processes perspective in the Balanced Scorecard encourages organizations to streamline operations continually. This can lead to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: Monitoring customer satisfaction scores over time helps businesses ensure that they are meeting customer needs and expectations. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and refer others.
- Employee Engagement: The learning and growth perspective emphasizes employee satisfaction and development. Engaged employees are more productive and contribute positively to an organization’s success.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: With a wealth of data generated by the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can make informed decisions rather than relying on guesswork.
How the Balanced Scorecard Drives Performance Improvement
The Balanced Scorecard acts as a crystal ball tool, presenting a holistic view of organizational performance and serving as a strategic communicator, enabling businesses to drive performance improvement effectively through the use of business performance management (BPM) and performance measurement tools.
One of the key benefits of the Balanced Scorecard is its ability to provide a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s performance across multiple perspectives. By considering financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, businesses gain a well-rounded understanding of their overall performance and can identify areas for improvement.
With the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can align their strategic objectives with specific metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs). These indicators help track progress and provide a clear measurement of success. For instance, organizations can measure revenue growth rate and customer satisfaction score to assess financial and customer perspectives respectively. By monitoring these KPIs, businesses can make data-driven decisions to improve performance and drive growth.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard also enhances strategic communication and alignment within an organization. It allows for a transparent and consistent flow of information, ensuring that everyone in the organization understands the strategic goals and how their individual efforts contribute to overall success. This alignment helps prioritize projects, drives accountability, and fosters a culture of performance improvement.
| Perspective | Key Performance Indicators |
|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue growth rate |
| Customer | Customer satisfaction score |
| Internal Processes | Cycle time |
| Learning and Growth | Employee satisfaction score |
Implementation and Tools for the Balanced Scorecard
The implementation of the Balanced Scorecard can be facilitated by utilizing various tools, including balanced scorecard templates, models, perspectives, and software, which provide businesses with the necessary resources to adopt and manage the strategy effectively.
One essential tool is the balanced scorecard template. This pre-designed framework allows organizations to structure their scorecards based on their specific needs and objectives. It provides a visual representation of the four perspectives, enabling businesses to align their strategic goals and performance measures accordingly. By using a balanced scorecard template, organizations can save time and ensure consistency in their scorecard design.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Balanced Scorecard Template | A pre-designed framework that helps structure performance measures |
| Balanced Scorecard Model | A comprehensive framework that guides the development of a balanced scorecard |
| Balanced Scorecard Perspectives | The four key areas of measurement: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth |
| Balanced Scorecard Software | Specialized software that automates the process of creating, managing, and analyzing balanced scorecards |
Another tool that organizations can leverage is the balanced scorecard model. This comprehensive framework serves as a guide for developing a balanced scorecard that aligns with the organization’s strategy. It helps businesses identify the most relevant and impactful performance measures for each perspective, ensuring a well-rounded assessment of organizational performance.
Balanced scorecard software is also available to streamline the implementation and management of the strategy. This specialized software automates the process of creating, managing, and analyzing balanced scorecards. It provides businesses with real-time insights and data visualization, enabling them to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions based on accurate information.
By using balanced scorecard templates, models, perspectives, and software, organizations can effectively implement and manage the Balanced Scorecard approach. These tools provide businesses with the necessary resources to align their strategic objectives, measure performance, and drive growth. With the right tools in place, businesses can unlock the full potential of the Balanced Scorecard strategy and achieve long-term success.
Tips for Effective Balanced Scorecard Implementation
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard successfully involves more than just tracking KPIs. Here are some tips to ensure effectiveness:
- Clear Strategic Objectives: Define your strategic objectives clearly and ensure they align with the organization’s mission and vision.
- Engage the Workforce: Involve employees at all levels in the process. When employees understand how their work contributes to the organization’s success, they are more motivated.
- Regular Review: Don’t just track KPIs; review them regularly. Identify trends and take action based on the data.
- Technology Utilization: Consider using Balanced Scorecard software to automate data collection and reporting, making the process more efficient.
- Training and Education: Invest in training and education for employees to enhance their skills and contribute to the learning and growth perspective.
- Balanced Scorecard Champions: Appoint champions within the organization who can drive the implementation process and ensure its success.
Remember that the Balanced Scorecard is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It should be tailored to your organization’s unique goals and needs. When implemented effectively, it becomes a powerful tool for unlocking success and driving continuous improvement.
The Role of Balanced Scorecard in Strategy Alignment
The Balanced Scorecard plays a crucial role in strategy alignment by ensuring organizational objectives are effectively aligned with strategic goals, facilitating the successful implementation of business strategies. This approach provides a holistic view of an organization’s performance, enabling leaders to make data-driven decisions and drive growth. By measuring performance across four key perspectives – financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth – the Balanced Scorecard helps organizations track their progress in a balanced way.
Strategic objectives are the foundation of the Balanced Scorecard, guiding organizations in defining their goals and determining the metrics that align with those goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to measure performance in each perspective, offering valuable insights into areas such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction, cycle time, and employee satisfaction. These metrics provide a clear understanding of how well the organization is performing in relation to its strategic goals.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard fosters strategic communication within the organization, ensuring that all stakeholders understand the objectives and their role in achieving them. It also helps in aligning the workforce by providing a shared framework for prioritizing projects and allocating resources. With improved organizational alignment, accountability is enhanced, as employees can clearly see how their individual efforts contribute to the overall success of the organization. The Balanced Scorecard also supports informed decision-making, helping leaders identify areas of poor performance and take corrective actions to improve results.
Table 1: Examples of Key Performance Indicators in Balanced Scorecard Perspectives
| Perspective | Examples of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue growth rate, return on investment (ROI), profit margin |
| Customer | Customer satisfaction score, Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate |
| Internal Processes | Cycle time, defect rate, process efficiency |
| Learning and Growth | Employee satisfaction score, training hours per employee, innovation rate |
To enhance the benefits of implementing the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can leverage technology solutions such as balanced scorecard software. These software tools, like Spider Impact, streamline the implementation and management of the Balanced Scorecard process. They offer features like automated data collection, real-time reporting, and interactive dashboards, making it easier for organizations to monitor performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Measuring and Evaluating Organizational Performance
The Balanced Scorecard provides a robust framework for measuring and evaluating organizational performance, leveraging performance management, key performance indicators (KPIs), performance metrics, and a comprehensive performance measurement framework to drive continuous improvement. It allows organizations to assess their performance from multiple perspectives, enabling a more holistic view of their operations and progress toward strategic goals.
One of the key components of the Balanced Scorecard is performance management, which involves setting clear objectives, monitoring progress, and taking corrective actions when necessary. By defining specific KPIs for each perspective, organizations can track their performance and identify areas that require attention or improvement. This data-driven approach ensures that organizations have the necessary information to make informed decisions and prioritize initiatives that will drive growth.
To effectively measure performance, organizations must establish relevant performance metrics. These metrics help translate strategic objectives into quantifiable measures that can be tracked and monitored over time. For example, from a financial perspective, metrics such as revenue growth rate and return on investment (ROI) can provide insights into the organization’s financial health and profitability. Similarly, from the customer perspective, metrics like customer satisfaction score and Net Promoter Score (NPS) can gauge the organization’s success in meeting customer needs and expectations.
| Perspective | Example KPIs |
|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue growth rate, ROI, cost per unit, profit margin |
| Customer | Customer satisfaction score, NPS, customer retention rate, market share |
| Internal Processes | Cycle time, defect rate, process efficiency, on-time delivery |
| Learning and Growth | Employee satisfaction score, training hours, employee turnover rate, innovation rate |
Conclusion
The Balanced Scorecard proves to be a highly effective strategic management tool, enabling businesses to achieve success by aligning objectives, measuring performance, and making data-driven decisions.
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) approach provides organizations with a holistic view of their performance across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. By using the BSC, organizations can measure their performance in a balanced way and gain valuable insights to drive growth.
The BSC allows organizations to define strategic objectives and align metrics with their goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to track progress in each perspective, such as revenue growth rate, customer satisfaction score, cycle time, and employee satisfaction score. This data-driven approach helps organizations make informed decisions and prioritize projects that align with their strategic objectives.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard not only improves strategic communication and aligns the workforce, but it also enhances organizational alignment and accountability. Employees gain a clear understanding of how their contributions impact the organization’s success, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment. Additionally, the BSC supports decision-making, helps improve poor performance, and enables organizations to adapt to changes in the market.
To maximize the benefits of implementing the Balanced Scorecard, organizations can leverage technology solutions such as balanced scorecard software, like Spider Impact. This software streamlines the process, making it easier to collect and analyze data, monitor performance, and generate insightful reports. By harnessing the power of technology, organizations can enhance their strategic management efforts and drive even greater success.





