Disclaimer: We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. For more information, visit our Disclaimer Page.
It is important to know how consumers will react when prices change. The Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) measures this relationship between two goods. It determines if they are more or less sensitive, providing valuable insight for companies optimizing their pricing strategy in different markets with varying economic conditions. Find out more below about this important measure!
What Is Cross Elasticity of Demand?
The cross elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded good to price changes on another product, ceteris paribus. For example, if Costa coffee increases by 30%, does this impact Starbucks’ demand?
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) measures the relationship between two goods when their prices change and calculates its effect on consumption levels. In other words, it calculates how the demand for one product is affected by the change in the price.
There are three types of goods in Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) – substitute, complementary and unrelated. To determine the relationship between these three types of goods, we can look at a few things: First, substitute goods compete for the same customers; second, complementary where one is consumed with another and their demand directly affects each others’ consumption; third unrelated which don’t affect price or quantity demanded when prices change in either direction.
Think of it this way: if one good is in greater demand when the price for another good goes down, they’re considered substitutes. If, on the other hand, an increase in prices for a particular product reduces the consumption of said products instead, then what you have are complementary goods.
Cross Price Elasticity Formula
The following equation is used to calculate Cross Price Elasticity of Demand XED:

- Qx = The average quantity between the previous and changed quantities is calculated as ( new quantity X + previous quantity X) / 2.
- Py = The average price between the previous and new prices, calculated as (new price y+ old price y) / 2.
- Δ = The change of price or quantity of product X or Y.
XED > 0 – A positive cross-price elasticity indicates that the two products (or services) are substitute goods.
XED < 0 – Negative Cross Price Elasticity means that the two products (or services) are complementary goods.
XED = 0 – The two products (or services) are unrelated.
3. Types of Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
Let’s look at three ways cross price elasticity of demand can be measured: positive elasticity, negative elasticity, and unrelated.
1. Cross-Price Elasticity of Substitute Products
Cross price elasticity of demand for substitute goods also knows positive cross-price elasticities happen when the demand for product A goes up with an increase of good B’s prices or vice versa.
If the price of one good increases, demand for a substitute product will increase as well. This type of relationship is known as positive cross-price elasticity, and it occurs when there exists a positive correlation between prices in products with close substitutes or related goods.
For example, if people tend to buy more Pepsi products during times of high Coke price, this is considered positive cross-price elasticity because both are substitutes on that market.
Categories of Substitute Products
Two goods that are substitutes like coffee and tea, have a positive cross elasticity of demand, meaning as the price for good Y rises (coffee), the quantity demanded of good X (tea) will rise.
There are two categories of substitute products: close substitutes and weak substitutes. Close substitutes have similar characteristics, features, or uses as the original product, whereas weak substitutions resemble but do not match the primary good completely.
Items with a positive but low cross-elasticity of demand are weak substitutes. This is often the case for different product substitutes, such as tea versus coffee. Conversely, substitutes that have high elasticities are considered strong.
Close Substitutes
When a minimal price increase of Coca-Cola causes an enormous demand for Pepsi, we can say that the two products are close substitutes. For example, this is shown in this graph:
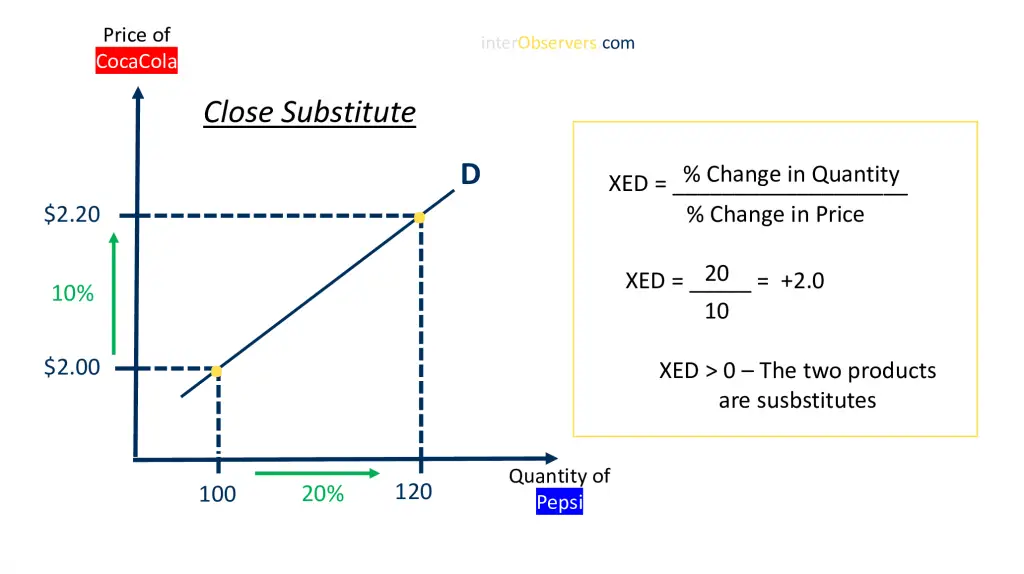
We can see from the chart above that there are positive correlations between close substitutes. This is because closely related goods have a strong relationship, so an increase in price for one good strongly affects the demand.
Weak Substitutes
The graph below shows that for weak substitutes, an increase of the price of tea by 10% will lead to only a 2% rise in demand for coffee. This is because cross-elasticity between these two products is low, and therefore, there is little change in consumer choices when prices fluctuate.
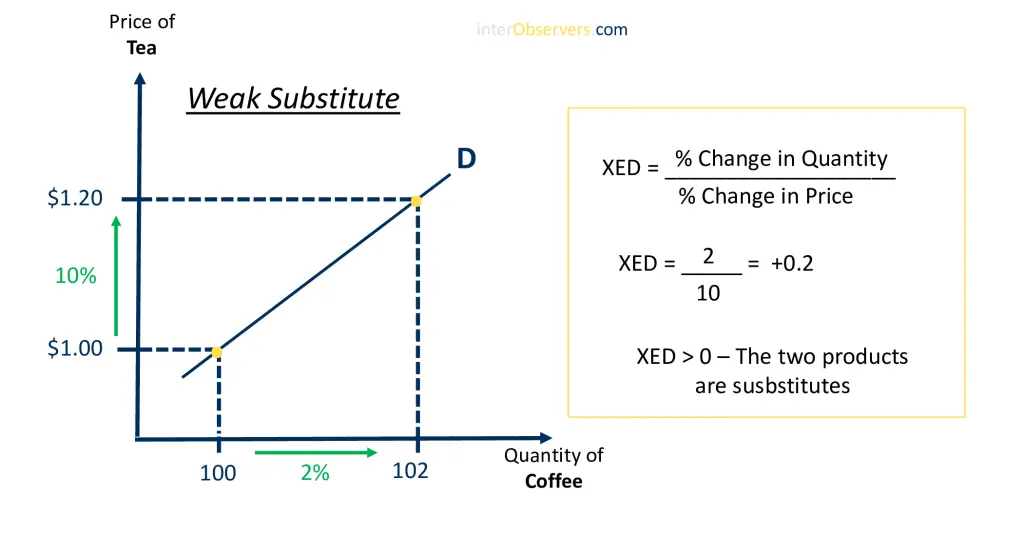
Weak substitute goods may still be related to each other, but it is not a substantial one. Still, these are considered substitutes products because they can ultimately provide the same purpose or function for consumers and businesses.
Note: The demand curve represents the correlation between price and quantity demanded certain goods or services.
2. Cross-Price Elasticity of Complementary Products
Two goods that complement each other have a negative cross elasticity of demand. This is because when the price for good Y goes up, people will want less X. A complementary product is typically one that people buy together and not separately due to their close connection with one another; they go hand in hand or fit into the same niche market (e.g., toothpaste & toothbrush).
When the cross price elasticity of demand is negative, each good or service serves as a complement for another. Thus, the absolute value isn’t used to demonstrate how much Good A’s quantity demanded will increase depending on Good B’s price.
Categories of Complementary Products
There are two types of complementary products: close and weak complements. Close complement goods typically go together, such as bread and butter or a computer printer. Weak complementary goods don’t always have to be used in tandem but tend to sell better when they work well together, like chocolate chip cookies and ice cream.
Close Complements
When the price of a product decreases, it typically leads to fewer people consuming that particular item. For example, there is an interesting correlation between tennis racket and tennis ball: if one increases, we see a large decrease in demand for its complement. A graph demonstrating this effect can be seen below.
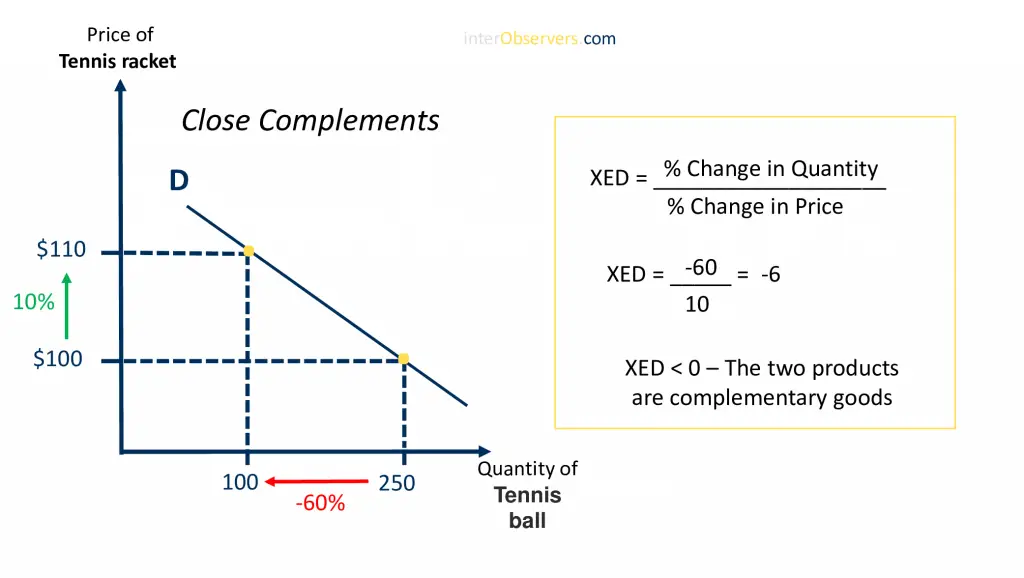
A graph shows the relationship between tennis rackets and tennis balls. As we can see from it, when there is a rise in the price of one product, demand for another will fall as well.
To summarize, you can’t buy tennis balls without first purchasing a tennis racket. Hence complementary goods rely on the other’s demand to exist.
Weak Complements
Weak complementary goods are not particularly sensitive to increases in the prices of other related products. On the contrary, they hardly respond at all. Thus, although there is a slight connection between weak complements and their associated product price changes, it’s minimal compared to close complement goods.
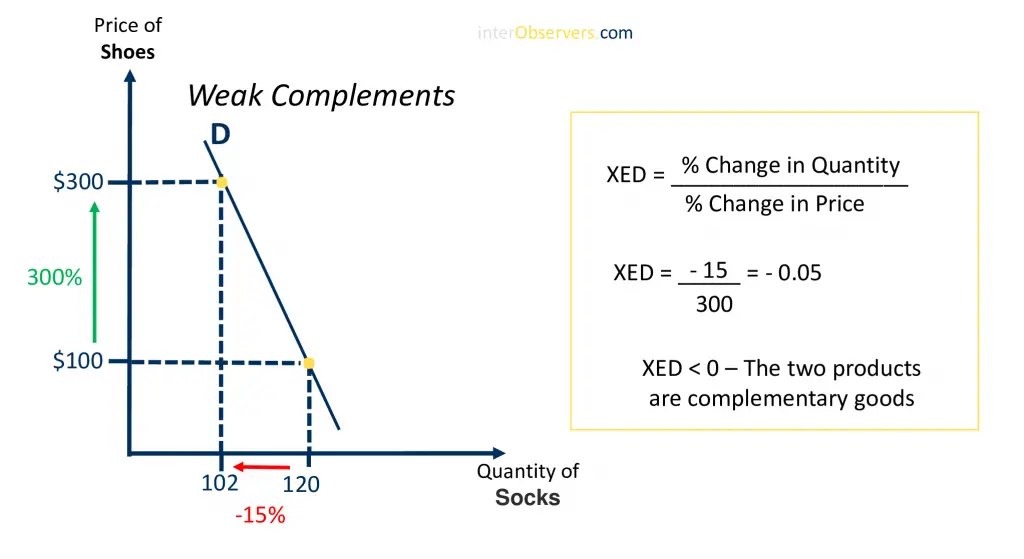
The graph below shows that a significant price increase for shoes results in a slight decrease in demand for socks. This phenomenon is called weak complementary goods. It can be seen by looking at the implementation of this relationship between prices and product demands within real-world examples—such as shoe sales decreasing slightly when socks are on sale or vice versa.
The relationship between two products is unrelated when one product’s price increase doesn’t affect the other. This means that independent goods have a zero cross elasticity of demand because their prices don’t influence each other.
For example, if we compare computers and apple, then an increased price in apples would have no impact on the number of computer sales; therefore, their cross-effect elasticity value is zero (a vertical line represents this graph).
When comparing these two items, they are completely independent or unrelated because one does not affect the demand.
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Example
Now, let’s compare the two fast-food chains. A 10 percent price increase at Mcdonalds did not go over well with consumers who decided to switch to Burger King instead–leading to a 5% rise in demand for BK products.
The formula for cross elasticity of demand is as follows:
- XED = % Change in Demand of X / % Change in Price of Y
So let’s start with finding our variables:
- ΔQx = 5 (Burger King saw a 5 percent increase in demand.)
- ΔPy = 10 (Mcdonald’s prices increased by 10 percent.)
- XED = 5/10 = 0.5
- XED > 0
The relationship between Mcdonald’s and Burger King is elastic. This means that the two are substitutes, so consumers will be willing to purchase more of the other good instead of increasing the price.
Why is Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Important?
Pricing Strategy
Small business owners can use cross elasticity of demand to determine the best price point for their products or services. The analysis will allow you to figure out how much revenue your company loses when raising prices and gains by lowering them, in addition to understanding if there are cheaper alternatives that customers might turn towards instead of buying from you. In addition, products without substitutes have more freedom to set up a good pricing strategy because they don’t need to lose potential sales due to alternative purchases being too close by.
Stay ahead of your competitors
Sometimes a complementary product/service is priced at a rate that reflects the understanding of its counterpart’s competitor. If, for example, there was an increase or decrease in one variant, it would be wise to create another version that will replace the old ones because customers are likely to look out for new products and services every time they purchase something.
Identify potential threats
If your business provides a product or service that doesn’t appear to have any current competitors, it’s important not to get overconfident. A decrease in the price of another complementary good could actually cause demand for yours to go down due to the negative cross elasticity of demand.
Organizational Strategy
A thorough analysis of the market and cross elasticity is key when deciding whether to launch a new business or expand your existing one.
Related Articles:
Conclusion
So, what does this all mean? Well, understanding the relationship between variables and how they affect each other is key to making good business decisions. For example, many factors go into calculating Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) for two goods – it’s not just about one change in price or demand for another good. When deciding on your marketing strategy and which channels to use, keep these principles in mind.
We hope this blog post has given you a better understanding of the Cross Price Elasticity of Demand (XED) and how it can be used to measure demand. The XED is important for marketers, economists, researchers, business professionals, and more because it helps us understand how different goods affect each other’s demand. Share or subscribe if you enjoyed our article!





