Disclaimer: We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. For more information, visit our Disclaimer Page.
The world of data is changing and growing at an unprecedented rate. Data is a driving force in our society. The ever-expanding volumes of data from many sources we now have access to have led organizations worldwide to rely on their data more than ever before.
One trend fueling this approach is the increasing availability and affordability of technology, which facilitates greater use for analytics purposes with precision, accuracy, and scalability, allowing businesses to grow exponentially.
Nowadays, organizations are in a constant state of flux and need to be agile enough to keep up with the fast-paced world. With this rise comes an increase in digital data, including emails and IoT devices that send text messages or collect information from sensors on your mobile phone.
Organizations can harness these raw data sources for analysis to stay ahead of their competitors. One example is IBM Watson Analytics which provides companies with insights and analytics.
Data management is a complex process, and there are many steps to manage it properly. This post will discuss what data lifecycle management is, the six phases of the lifecycle of data, the three main goals of data lifecycle management, and more!
Data Lifecycle Management Definition
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is the different stages that data goes through during its life, from when it’s created to when it’s deleted. Data lifecycle stages include creation, utilization, sharing, storage, and deletion. Each stage of the data lifecycle will be controlled by different policies that control protection, resiliency, and regulatory compliance.
What is Data Lifecycle Management?
Data lifecycle management is a comprehensive approach to managing an organization’s data. It operates according to policy-based systems that manage the flow of information across different applications, systems, databases, and storage media during its life cycle, from creation through retirement.
Data Lifecycle Management is a way to make your data most valuable. There are many definitions, but one thing remains true: Data Lifecycle Management is not a specific product but rather an effective way for organizations from all industries to leverage their most valuable asset – DATA!
The data lifecycle management process ensures that the organization can understand inventories, maps, and controls its data throughout as it’s created, modified, and stored in addition. In addition, it will ensure that the most helpful and recent records are accessible with speed and ease because much of this process can be automated into repeatable steps.
Data is a precious resource that needs to be understood and managed from the moment it’s created. Data lifecycle management (DLM) helps organizations do this by moving data through different lifecycle stages, adapting its usage at each stage following current business requirements.
Understanding how information moves between these phases allow you to manage your company’s finances better and understand what type of Big Data investments may make sense for your organization today and tomorrow.
The Significance of Enterprise Data Storage in DLM
In today’s digital era, enterprise data storage stands as a cornerstone of effective data lifecycle management. As organizations generate vast amounts of data daily, the need for robust and scalable storage solutions becomes paramount. These storage solutions not only house the data but also ensure its availability, integrity, and security.
Modern enterprise data storage systems offer features like real-time data replication, automated backups, and advanced encryption mechanisms. These features ensure that data remains accessible and protected against unforeseen disasters or cyber threats. Furthermore, with the advent of cloud storage solutions, organizations can now scale their storage needs dynamically, ensuring cost-effectiveness and flexibility.
Incorporating a robust enterprise data storage solution within the DLM process ensures that data is not just stored, but it’s stored wisely, securely, and in a manner that aligns with the organization’s operational and strategic goals.
The Six Phases of the Lifecycle of Data
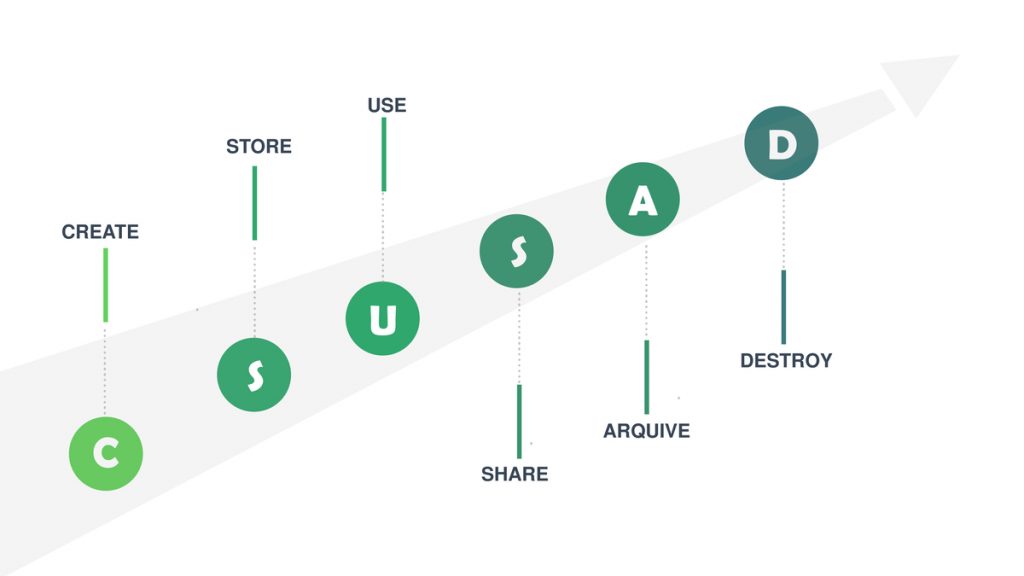
→ Data capture
The first step in the data lifecycle is creating and then capturing it. There are several ways to do this, but we focus on three: getting existing data that outside entities have created; using human-driven input and other devices from your own business; or collecting information through sensors, Internet of Things elements (IoT), external databases, etc.
→ Data maintenance or storage
This is the organization, cleansing, and synthesis of entry signals. Data maintenance means that you are processing data to make it usable. The data has to be stored in places that fit them. This is important because organization, access, and data control are essential for a company’s success.
→ Data usage
Data is a raw material used for various activities such as alterations, analysis, storage, and decision-making. Once data has been adequately maintained, it becomes information or knowledge to achieve your needs.
→ Data publication
Data publication or release is making data available to a broader audience. Data publishing often refers to sharing outside your enterprise and releasing it into the public domain with few restrictions when all appropriate authorities have approved them.
→ Data archiving
Data that have either not been used recently or need to be archived and indexed for future use are stored differently during this phase. Data archival means storing those data in a different location that the organization no longer requires; however, it is kept here if needed to avoid facing any problems.
→ Data deletion
This consists of deleting duplicated data, which are eliminated to prevent the generation of statistical noise or the appearance of errors. It is the last stage in the data lifecycle. Data deletion refers to permanently destroying unnecessary data from storage and archives, meaning that it is deleted from the system entirely and removed for good.
What are the Three Main Goals of Data Lifecycle Management (DLM)?
One of the top challenges companies faces when they grow and accumulate data is a data breach, which means that the data must be managed effectively throughout its lifecycle.
Managing data is challenging. Data lifecycle management has goals that need to be considered. These goals are essential for an unhindered and streamlined flow of information.
Three main goals that need to be considered when managing the database throughout its lifecycle can be categorized as follows:
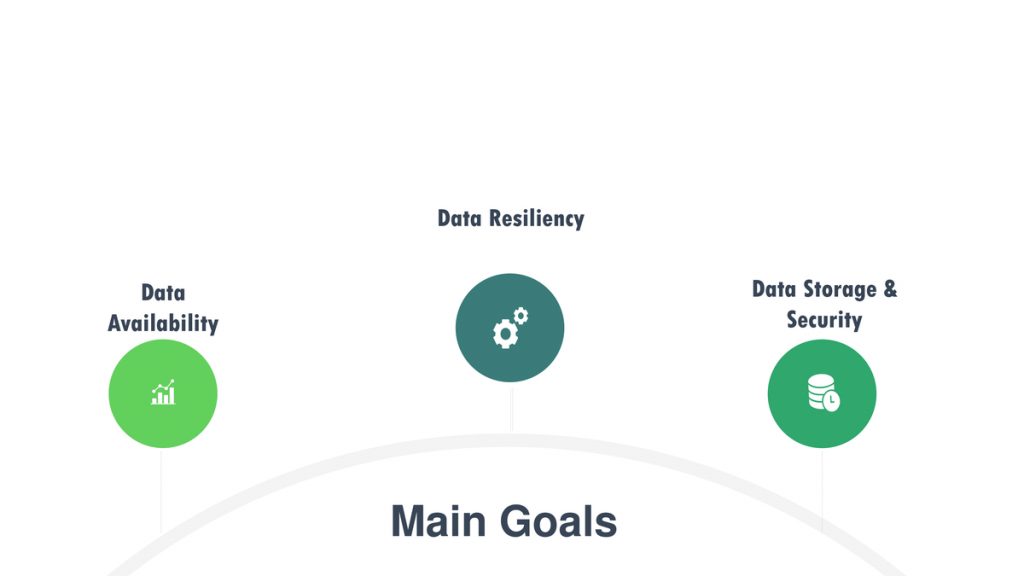
• Data Availability
The availability of data is imperative for the success of any project. Data unavailable when it needs to be accessed can lead to cascading failures in other processes that depend on this data from a previous process. In other words, ensuring your database has all available and accessible information instantly will make management easier while preventing devastating errors later.
Avoiding these failures requires careful consideration of all available options. One such option includes cloud-based solutions, which have shown themselves capable enough to meet your needs while being more accessible than local databases with limited bandwidth capabilities.
Data often drives businesses, so it’s crucial to ensure that the data is available and processed correctly.
• Data Resiliency
Data is very versatile and can be used in many different areas. Therefore, it’s essential to keep it organized to use the data effectively when needed. Additionally, you want your organization’s data consistent with all its users, which will help them access accurate information whenever they need it!
Data can change over time, whether through alterations or modifications. This can result in data sprawl, where the same information is present on different systems and devices in slightly different forms. Therefore, it’s necessary to put an infrastructure in place to ensure the integrity and performance of data.
Data integrity is at risk if various users allow simultaneous access to a database or the other backups are not adequately controlled in secure environments.
• Data Security and Confidentiality
Once you have acquired the data, it needs to be stored safely. Structured data is typically held in an on-site or clouded database, while unstructured data is stored on file servers and/or in the cloud. Regardless of where it’s being stored, this data should be securely protected against access by unauthorized users.
Data is the new currency, and many risks come with it; therefore, organizations should take risks seriously and keep their data secure by deploying a firewall system with antivirus software to prevent intrusion or danger from potential malware infections.
The potential value of regulated and black markets makes maintaining appropriate access crucial, especially given recent GDPR or personal data regulations.
What is Hot, Warm, and Cold Data?
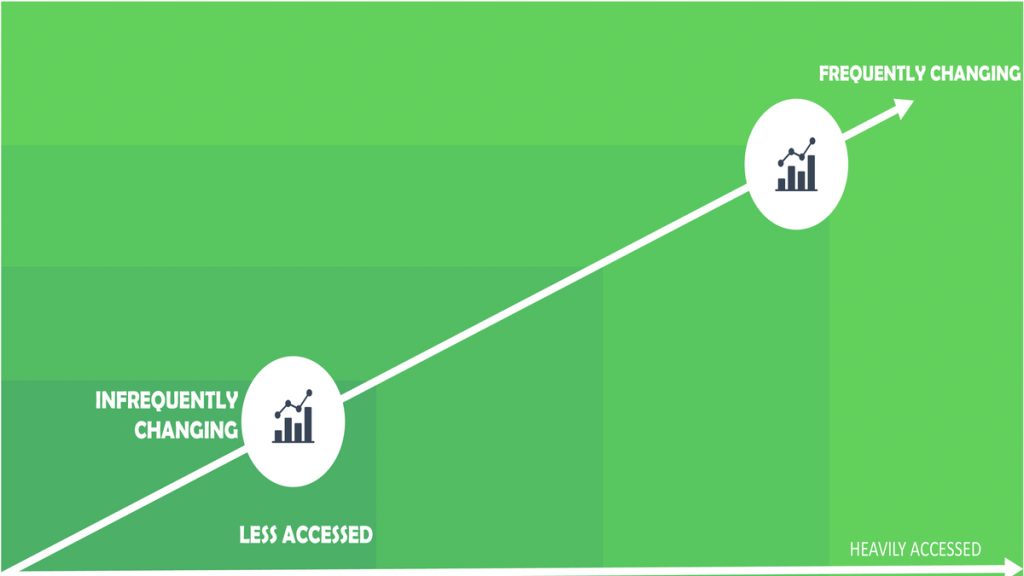
In its life, data is frequently classified according to a multi-temperature scale. The hot data is the most accessed, which needs to be replaced occasionally for decreased performance and business productivity. Warm data is still important but not as frequently accessible. Cooling data has ephemeral importance with little necessary use or access.
- Data heavily accessed and used daily for business activities are known as hot data. This type of data typically remains on Tier 1 storage, the most expensive, because it is optimized to deliver fast access times.
- However, data used infrequently must be available online to satisfy specific business rules and regulatory requirements. This data is referred to as warm data.
- Data that no longer has an intrinsic value to the business is considered cold data. Cold data is usually archived or deleted.
Conclusion
As you can see, data lifecycle management is a critical process for any business. By understanding the six phases of the data lifecycle and the three main goals of data lifecycle management, you can ensure that your data is properly managed and used to its full potential.
We hope you found this post helpful. Be sure to subscribe to our newsletter to stay up-to-date on the latest data management and storage news, tips, and tricks. As always, if you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to us. Thanks for reading!





